Colon cancer is the malignant growth of tumor cells in the large intestine. It is the third most common cancer and has the fourth highest death rate out of all types of cancer. Current treatments are limited, as they can be painful for the patient by killing healthy cells alongside cancer cells, and there is no guarantee that the treatments will completely eliminate all cancer cells.
Ferroptosis is a type of programmed cell death caused by high intracellular iron levels, which in turn activates cell death pathways. It differs from traditional cell death, apoptosis, since it is triggered by high iron intracellular concentrations. Rather than affecting the cell’s genetic material or plasma membrane, ferroptosis causes cell death through shrinking mitochondria and increasing mitochondrial membrane density.
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a type of RNA that does not code for protein synthesis. While they don’t code for protein, lncRNAs have other functions, such as controlling gene regulation through unwinding chromatin for transcription and consequent translation and RNA processing. In regards to cancer, lncRNAs have been proven to contribute to proliferation, metastasis, and reproduction of malignant cells, and can therefore be indicators of the disease and its prognosis. Ferroptosis-related lncRNAs (FRLs), which influence the titular cellular process, in particular have been identified as possible indicators of cancer prognosis, yet not much is known.
The purpose of Wu et al (2022)’s study was to determine the molecular functions of FRLs in colon cancer. In this experiment, RNA sequencing data and genes related to ferroptosis were obtained from databases. In addition, human intestinal epithelial cells and various human colon cancer cell lines and colon cancer cell samples taken from patients at the Gastrointestinal Surgery Department of Xiangya 3rd Hospital were tested for cell composition via CIBERSORT, and had their RNA extracted for qRT-PCR and analysis. Malondialdehyde (MDA), Fe2+, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and IC50 levels of various drugs were also tested in these cells, as they all have a role in controlling ferroptosis and the consequent cell death. It was found that 26 different FRLs had some relationship to colon cancer, most of them being risk genes, genes specifically associated with the onset of cancer. Two lncRNAs, AP003555.1 and AC005841.1, had a significant relationship to colon cancer, as seen by the increased MDA, Fe2+, and ROS levels in cells with those two lncRNAs silenced and their knockout inhibiting cell proliferation.
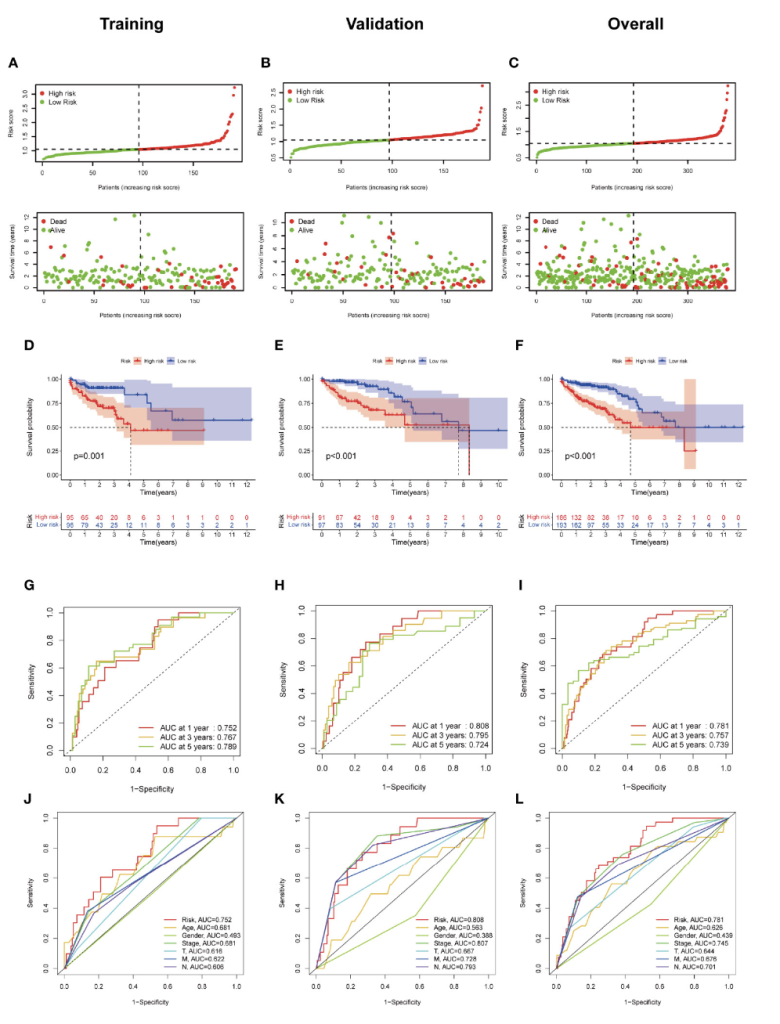
Figure 1: Construction and validation of the ferroptosis-related lncRNA signature model in the training cohort, validation and overall groups. (A–C) The distribution of the risk scores and the distributions of overall survival status and risk score in the training, validation and overall groups. (D–F) The Kaplan–Meier curves for survival status and survival time in the training, validation and overall groups. (G–I) The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve shows the potential of the prognostic ferroptosis-related lncRNAs signature in predicting 1-, 2-, and 3-year overall survival (OS) in the training, validation and overall groups. (J–L) AUC of ROC curves comparing the prognostic accuracy of the risk score and other prognostic factors in the training, validation and overall groups.
Sources
Li, Jie, Feng Cao, He-liang Yin, Zi-jian Huang, Zhi-tao Lin, Ning Mao, Bei Sun & Gang Wang (2020), Ferroptosis: past, present and future, Cell Death and Disease, Volume 11, Issue 2, Page 88
Mármol, Inés, Cristina Sánchez-de-Diego, Alberto Pradilla Dieste, Elena Cerrada, and María Jesús Rodriguez Yoldi (2017) Colorectal Carcinoma: A General Overview and Future Perspectives in Colorectal Cancer, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, Volume 18, Issue 1, Pages 197.
Qian, Yuchen, Lei Shi, and Zhong Luo (2020) Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy, Frontiers in Medicine
Wu, Zhiwei, Zhixing Lu1, Liang Li, Min Ma, Fei Long, Runliu Wu, Lihua Huang, Jing Chou, Kaiyan Yang, Yi Zhang, Xiaorong Li, Gui Hu, Yi Zhang, and Changwei Lin (2022) Identification and Validation of Ferroptosis-Related LncRNA Signatures as a Novel Prognostic Model for Colon Cancer, Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy, Volume 12
Yao, Run-Wen, Yang Wang & Ling-Ling Chen (2019) Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs, Nature Cell Biology, Volume 21, Issue 5, Pages 542-551
Yu, Haitao, Pengyi Guo, Xiaozai Xie, Yi Wang, and Gang Chen (2017) Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death, and its relationships with tumourous diseases, Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Volume 21, Issue 4, Pages 648–657
Zhang, Kaiming, Liqin Ping, Tian Du, Gehao Liang, Yun Huang, Zhiling Li, Rong Deng, and Jun Tang (2021) A Ferroptosis-Related lncRNAs Signature Predicts Prognosis and Immune Microenvironment for Breast Cancer, Frontiers in Molecular Bioscience